4 difference between a traditional and Roth 401(k) – Traditional 401(k)
A traditional 401(k) is the more commonly recognized type of 401(k) plan. With a traditional 401(k), your contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, meaning the money is deducted from your paycheck before income taxes are calculated. This results in a lower taxable income for the current year, potentially reducing your overall tax liability.
Key features of a traditional 401(k):
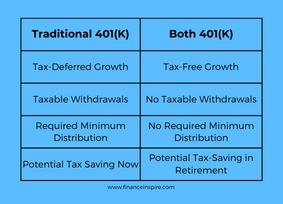
1. Tax-Deferred Growth: The money contributed to a traditional 401(k) grows tax-deferred, meaning you don’t have to pay taxes on the investment gains until you withdraw the funds in retirement.
2. Taxable Withdrawals: When you start taking distributions from your traditional 401(k) during retirement, the withdrawals are subject to ordinary income tax rates at that time.
3. Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Once you reach age 72 (or 70 1/2 if you turned 70 1/2 before January 1, 2020), you must begin taking required minimum distributions (RMDs) from your traditional 401(k) each year, regardless of whether you need the income or not.
4. Potential Tax Savings Now: By reducing your taxable income today, a traditional 401(k) can provide immediate tax savings, which can be beneficial if you expect to be in a lower tax bracket during retirement.
4 difference between a traditional and Roth 401(k) – Roth 401(k)
A Roth 401(k) is a relatively newer addition to the 401(k) landscape, first introduced in 2006. Unlike a traditional 401(k), contributions to a Roth 401(k) are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you don’t receive an upfront tax deduction.
Key features of a Roth 401(k):
1. Tax-Free Growth: The money contributed to a Roth 401(k) grows entirely tax-free, and qualified withdrawals in retirement are also tax-free.
2. No Taxable Withdrawals: Since you’ve already paid taxes on your contributions, you won’t owe any additional taxes on withdrawals from a Roth 401(k) in retirement, as long as you meet certain requirements.
3. No Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Unlike a traditional 401(k), you are not required to take minimum distributions from a Roth 401(k) during your lifetime, allowing your money to continue growing tax-free.
4. Potential Tax Savings in Retirement: By paying taxes on your contributions now, a Roth 401(k) can provide significant tax savings during retirement, especially if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket at that time.
Key Differences
The primary difference between a traditional and Roth 401(k) lies in the timing of when you pay taxes on your contributions and investment earnings.
With a traditional 401(k), you receive an upfront tax deduction, but you’ll have to pay taxes on your withdrawals in retirement. Conversely, with a Roth 401(k), you pay taxes on your contributions now, but your withdrawals in retirement are tax-free (as long as certain requirements are met).
Another key difference is the treatment of required minimum distributions (RMDs). Traditional 401(k) accounts are subject to RMDs, which can have tax implications and force you to withdraw funds even if you don’t need the income. Roth 401(k) accounts are not subject to RMDs during the account owner’s lifetime, allowing the funds to continue growing tax-free for as long as possible.
The fourth key difference is the income limits. There are no income limits to contribute to a traditional 401(k), but there are income limits to contribute to a Roth 401(k). If your income exceeds a certain threshold, you may not be eligible to contribute to a Roth 401(k).
Which Option is Right for You?
The choice between a traditional and Roth 401(k) ultimately depends on your individual circumstances, including your current and expected future tax brackets, retirement timeline, and overall financial goals. It’s important to understand the 4 differences between a traditional and Roth 401(k).
If you expect to be in a lower tax bracket during retirement, a traditional 401(k) may be more advantageous, as it provides an upfront tax deduction and potentially lower tax rates on withdrawals. However, if you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in retirement, a Roth 401(k) could be a better option, as you’ll pay taxes on your contributions now, but enjoy tax-free withdrawals later.
It’s also important to consider your time horizon and the potential for tax-free growth. The longer your money has to compound in a Roth 401(k), the more significant the tax-free growth potential becomes.
For younger workers with many years until retirement, a Roth 401(k) can be an attractive choice, as it allows them to take advantage of decades of tax-free growth and potentially higher incomes in retirement.
Ultimately, the decision between a traditional and Roth 401(k) should be made in the context of your overall retirement savings strategy and in consultation with a qualified financial advisor who can analyze your specific situation and provide personalized guidance.
Maximizing Your Retirement Savings
Regardless of whether you choose a traditional or Roth 401(k), it’s essential to take advantage of any employer-matching contributions, as these essentially represent free money that can significantly boost your retirement savings.
Additionally, consider diversifying your retirement savings across different account types, such as IRAs or taxable investment accounts, to optimize your tax strategy and provide flexibility in retirement.
Building a secure retirement requires a long-term mindset and a well-crafted savings plan. By understanding the differences between a traditional and Roth 401(k), and leveraging the appropriate account types for your specific circumstances, you can position yourself for a more financially secure future and enjoy the retirement lifestyle you envision.