Understanding the Crucial 3 Differences Between Fixed and Variable Interest Rate
In the world of finance, Interest rates, like those on personal loans, influence borrowing costs and investment returns. Fixed and variable rates are the two main types, each impacting borrowers and investors differently. This article explores the 3 key distinctions between fixed and variable interest rates for personal loans, empowering you to make informed financial decisions. We’ll delve into “3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate” – focusing on stability, predictability, and long-term costs – to help you choose wisely for your personal loan.
What is a Fixed Interest Rate?
A fixed interest rate, also known as the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, remains constant for the entire duration of a loan or investment. It does not fluctuate, regardless of market conditions or economic factors. This rate offers stability and predictability, allowing borrowers to accurately calculate their monthly payments. For investors, it ensures they can anticipate their expected returns over the agreed-upon term.
Advantages of Fixed Interest Rates
1. Certainty and Budgeting: With a fixed interest rate, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, borrowers can plan their finances more effectively, as their monthly loan payments remain the same throughout the life of the loan. This stability can be particularly beneficial for individuals with a fixed income or those who prefer predictable expenses.
2. Protection Against Rising Interest Rates: When interest rates rise in the market, borrowers with fixed-rate loans, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, are shielded from the impact, as their interest rate remains unchanged. This can result in significant savings over the long run, especially for long-term loans like mortgages.
3. Consistent Returns for Investors: Investors who hold fixed-rate investments, such as bonds or fixed-rate savings accounts, can expect a consistent stream of returns with the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, making it easier to plan their financial strategies and manage their portfolios.
Disadvantages of Fixed Interest Rates
1. Opportunity Cost: If market interest rates decline after securing a fixed-rate loan or investment with the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, borrowers or investors may miss out on the potential benefits of lower rates, as they are locked into the agreed-upon fixed rate.
2. Limited Flexibility: Fixed-rate loans or investments with the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate typically have limited options for renegotiating or refinancing without incurring additional costs or penalties.
3. Potentially Higher Initial Rates: In some cases, fixed interest rates or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate may be higher than variable rates at the time of origination, as lenders and investors factor in the risk of future rate fluctuations.
What is a Variable Interest Rate?
A variable interest rate, also known as an adjustable or floating rate, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, is one that fluctuates over time based on changes in market conditions or an underlying benchmark rate. This rate is typically tied to an index, such as the prime rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR), and adjusts periodically according to the movements of that index.
Advantages of Variable Interest Rates
1. Potential for Lower Initial Rates: Variable interest rates, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, often start lower than fixed rates, making them an attractive option for borrowers seeking more affordable initial payments or investors seeking higher initial yields.
2. Ability to Benefit from Falling Rates: If market interest rates decline, borrowers with variable-rate loans or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate can take advantage of lower payments, while investors holding variable-rate investments may see their returns increase.
3. Flexibility: Variable-rate loans and investments, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, typically offer more flexibility in terms of renegotiation or refinancing, as the terms can be adjusted to reflect current market conditions.
Disadvantages of Variable Interest Rates
1. Uncertainty and Budgeting Challenges: The fluctuating nature of variable interest rates, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, can make budgeting and financial planning more challenging, as payments or returns can change over time, sometimes significantly.
2. Exposure to Rising Interest Rates: If market interest rates rise, borrowers with variable-rate loans or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate may face higher monthly payments, potentially straining their budgets. Similarly, investors holding variable-rate investments may experience lower returns.
3. Potential for Interest Rate Caps or Floors: Some variable-rate loans or investments, or the 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate, may have caps or floors, limiting the extent to which rates can fluctuate, potentially reducing the benefits or drawbacks associated with variable rates.
Choosing Between Fixed and Variable Interest Rates: 3 Difference Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate
3 Difference Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate: The decision to opt for a fixed or variable interest rate depends on various factors, including your financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
When to Choose a Fixed Interest Rate
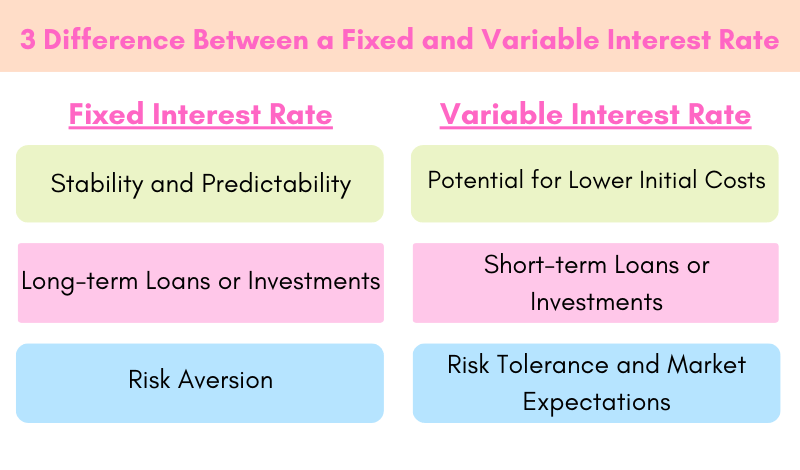
1. Stability and Predictability: If you value certainty and want to budget effectively for your monthly payments or expected returns, a fixed interest rate may be the preferred choice.
2. Long-term Loans or Investments: For long-term financial commitments, such as mortgages or long-term bonds, a fixed interest rate can provide protection against potential interest rate increases over the life of the loan or investment.
3. Risk Aversion: If you have a low tolerance for risk and prefer to avoid potential fluctuations in your payments or returns, a fixed interest rate can offer peace of mind.
When to Choose a Variable Interest Rate
1. Potential for Lower Initial Costs: If you are looking for lower initial payments or higher initial yields, a variable interest rate may be appealing, especially if you anticipate market rates remaining stable or declining in the near future.
2. Short-term Loans or Investments: For short-term financial commitments, where interest rate fluctuations may be less significant, a variable interest rate can provide flexibility and the opportunity to benefit from potential rate decreases.
3. Risk Tolerance and Market Expectations: If you have a higher risk tolerance and expect market interest rates to decline over the life of your loan or investment, a variable interest rate may be a suitable choice.
Conclusion: 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate
3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate – Understanding the difference between fixed and variable interest rates is crucial for making informed financial decisions. “3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate” – Stability, predictability, long-term costs. Learn the key distinctions between fixed vs adjustable rates to choose wisely for your mortgage.
“3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate” – Stability, predictability, long-term costs. Learn the key distinctions between fixed vs adjustable rates to choose wisely for your mortgage. 3 Differences Between a Fixed and Variable Interest Rate.